What is Fraud Detection?
Fraud Detection is a technology capable of monitoring transactions and customer behavior to identify and prevent financial fraud that could cause severe losses. This technology relies on enterprise tools, policies, and procedures to function effectively. When integrated into the Anti-Money Laundering (AML) framework—a set of regulations, policies, and laws aimed at preventing illegal laundering of money—Fraud Detection is referred to as Fraud and Anti-Money Laundering (FRAML).
>>> READ NOW: What Are AI Agents? The Difference Between AI Agents and AI Chatbots
Why is Fraud Detection Important?
Companies use Fraud Detection systems to minimize financial losses and maintain positive customer relationships. In many regions, implementing anti-fraud programs is not just an option but a legal requirement.
- In the US: Some states require insurance companies to have specific anti-fraud measures. For example, Texas mandates insurers to submit anti-fraud plans for approval, including procedures for investigating suspicious claims and training employees. These plans must be updated annually and resubmitted. Companies must designate a person responsible for overseeing compliance and maintaining records of fraud investigations and prevention measures.
- In the UK: The “Failure to Prevent Fraud” offense, enacted in April 2023, holds companies liable if their employees commit fraud without effective prevention programs. Additionally, from June 7, 2023, the UK’s Payment Systems Regulator (PSR) requires companies to reimburse customers victimized by Authorized Push Payment (APP) fraud.
Fraud Detection not only ensures compliance but also plays a critical role in protecting customers’ transactions and accounts. By preventing fraud before or as it occurs, organizations can mitigate losses promptly. According to the FBI, elderly victims in the U.S. lost an average of $35,101 per person to fraud in 2022, with total losses exceeding $3 billion. Globally, fraud losses surpassed $55 billion in 2021, mainly through cross-border transactions enabled by illegal technologies.
As fraud becomes more diverse and complex, companies must prepare for new regulations and enforcement measures. Integrating Fraud Detection into overall risk management frameworks helps companies protect consumers, reduce losses, ensure compliance, and combat financial crime more effectively.
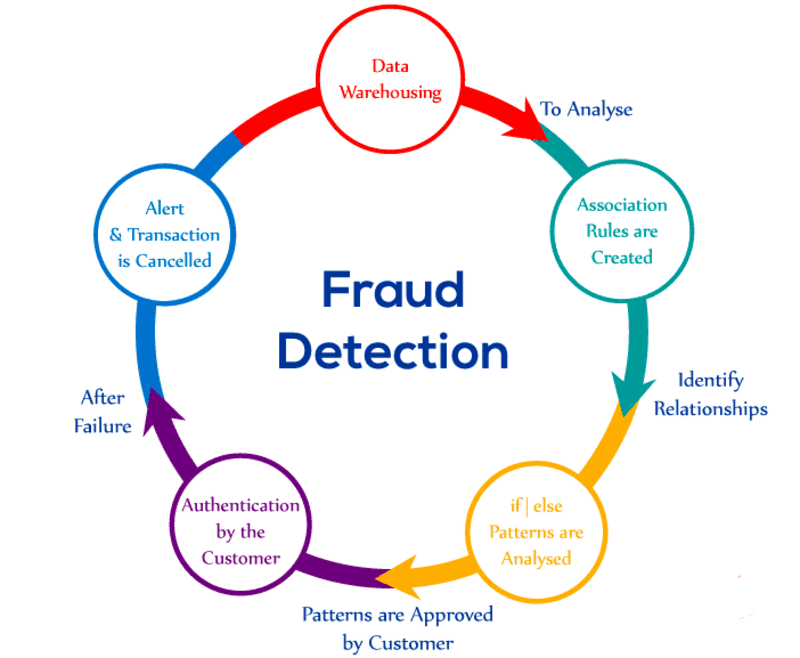
How Does Fraud Detection Work?
Before implementing a Fraud Detection system, a company’s dedicated fraud prevention team conducts a Risk Management Assessment to identify functional areas vulnerable to fraud. The team assigns Risk Scores to evaluate the likelihood and impact of potential fraud, prioritizing the most significant risks. They then assess Fraud Detection solutions suitable for addressing identified threats based on their type and severity.
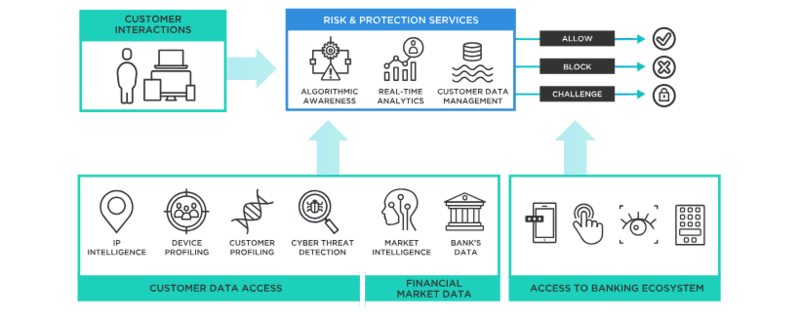
Common Fraud Detection Techniques including:
- Transaction Monitoring: Transaction monitoring tools automate Fraud Detection by analyzing transaction flows in real time. These tools perform identity verification and account authentication to stop fraudulent transactions as they occur. They also detect unusual patterns or behaviors, such as transaction frequency, amounts, geographic location, or value, to flag suspicious activities for further investigation.
- Statistical Data Analysis: Fraud Detection doesn’t always occur in real time. Statistical data analysis identifies fraud retrospectively by examining historical data. Techniques like data mining, regression analysis, and data analytics help investigators detect and isolate fraud patterns in large datasets. Tools like probability distributions and data matching pinpoint where and when fraud occurred or might occur in the future.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Many organizations now use AI and machine learning to enhance Fraud Detection. Neural networks, a type of machine learning model, can monitor transactions, analyze data, and detect or predict fraudulent behaviors faster and more effectively than traditional methods. Neural networks continuously learn from new data, improving their detection capabilities over time.
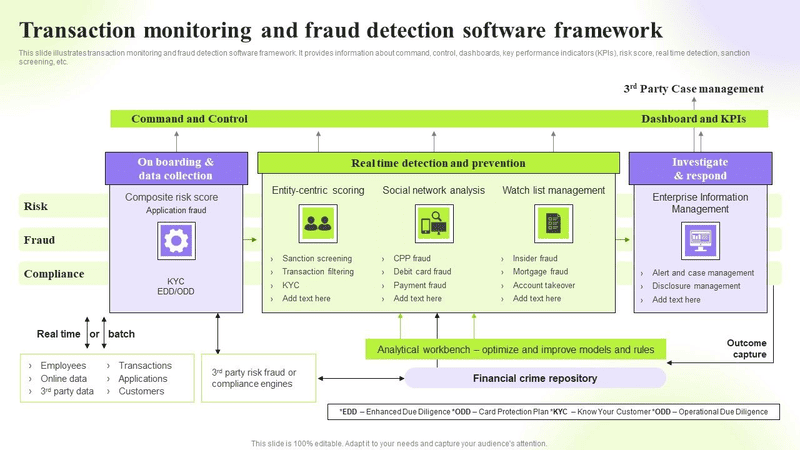
Common Types of Fraud Detection
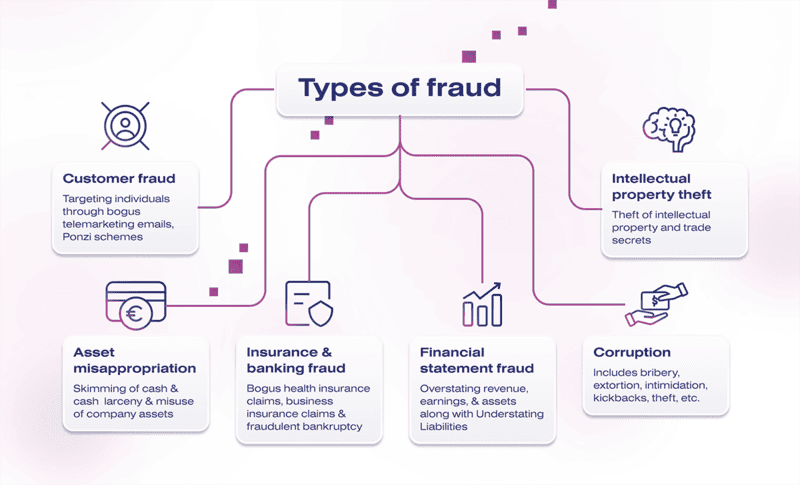
Fraud can appear in various forms, and new types of fraud continuously emerge. Some forms of fraud persist because they exploit vulnerabilities in company processes and systems. Common fraud tactics include:
- Payment Fraud: Payment fraud occurs when a fraudster obtains someone else’s payment information and performs unauthorized transactions. This type of fraud not only causes direct losses but can also lead to other fraudulent activities, as stolen payment information may be used for money laundering or cybercrime.
- Return Fraud: Return fraud exploits retailers’ return policies to illegitimately claim refunds. This type of fraud is often committed by individuals. Fraudulent returns may involve stolen goods, counterfeit items, used or pre-owned products, or items purchased from other retailers.
- Automated Clearing House (ACH) Fraud: ACH refers to the method of transferring funds between bank accounts, typically for businesses and organizations. ACH fraud occurs when fraudsters use bank account numbers to commit fraud, such as impersonating employees to change beneficiary account details and steal funds.
- Chargeback Fraud: Chargeback fraud happens when individuals dispute completed transactions to claim refunds. Although companies can contest fraudulent refund requests, these disputes still burden company resources, whether or not the claims are upheld.
- Account Takeover Fraud (ATO): Account takeover fraud occurs when a fraudster gains unauthorized access to an online account, such as a bank account, mobile account, or e-commerce account. The fraudster then uses the account to conduct unauthorized transactions without the consent of the account holder or issuing organization.