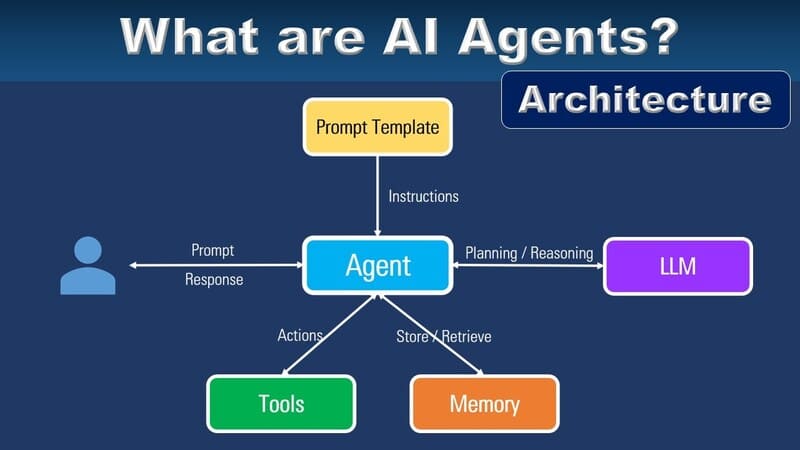
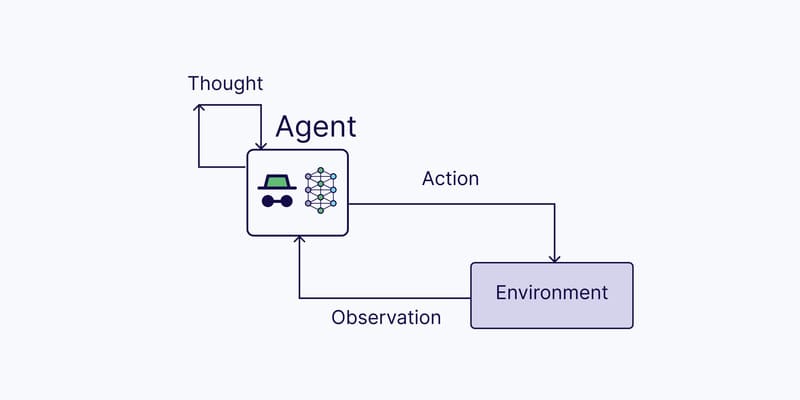
Generative Artificial Intelligence (Generative AI) is a rapidly evolving field that combines advanced machine learning techniques, big data, and powerful computational models to create new content that mimics human creativity. With the potential to revolutionize industries from entertainment to healthcare, understanding the concepts, applications, and technologies behind Generative AI is crucial for anyone interested in the future of artificial intelligence. Let’s dive into it with FPT.AI.
What is Generative AI?
Generative Artificial Intelligence, or Generative AI, is a new branch of AI (Artificial Intelligence) that can generate entirely new data or content. Unlike traditional AI models focused on prediction or classification, Generative AI can grasp the underlying structures and relationships within a dataset thanks to deep learning models, particularly neural networks trained on massive datasets.
In other words, Generative AI can learn the distributions and characteristics of the content it aims to create, then generate new outputs that resemble or even improve upon human-created content.
>>> EXPLORE: What Are AI Agents? The Difference Between AI Agents and AI Chatbots
Types of Generative AI Models
Each type of Generative AI model uses different approaches and serves various applications. Here are some of the most popular models:
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
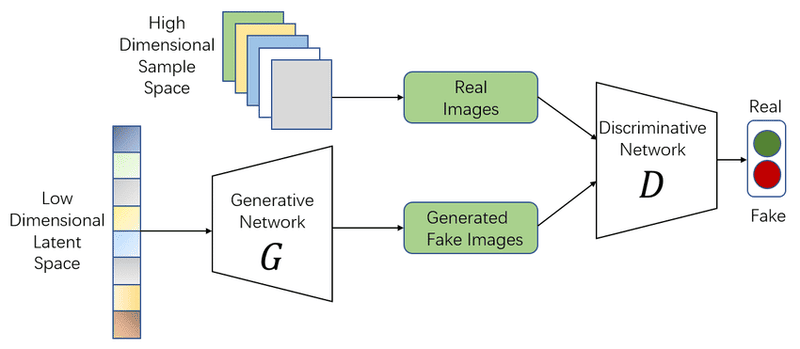
Introduced by Ian Goodfellow and colleagues in 2014, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are among the most prominent models in Generative AI. GANs consist of two opposing neural networks: the Generator and the Discriminator.
The Generator creates new data samples, while the Discriminator evaluates and distinguishes them from real data. Through this adversarial process, GANs progressively generate higher-quality data. GANs are commonly used for generating images, videos, and realistic artworks.
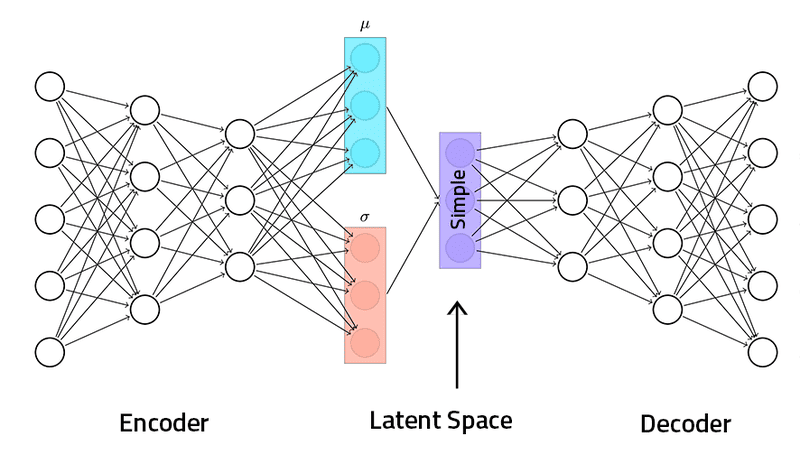
Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)
Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) are another widely used generative model for creating images, sounds, and even text. VAEs operate by encoding data into a latent space and then decoding it back into the original data.
Compared to GANs, VAEs offer more controlled and interpretable outputs. This makes them particularly useful for tasks like image manipulation, style transfer, and generating data based on specific attributes.
Transformer Models
Transformer-based architectures, particularly large language models like GPT (Generative Pretrained Transformer), have become central to the development of Generative AI. Unlike GANs and VAEs, Transformer models are designed to process sequential data, making them particularly effective for text generation and natural language processing (NLP).
Models like GPT-3, GPT-4, and T5 have been trained on vast text corpora and are capable of generating coherent, contextually relevant text, answering questions, writing essays, and even composing poetry.
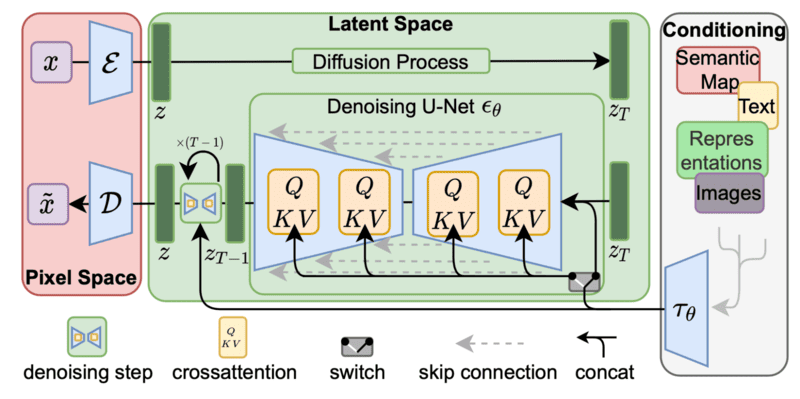
Diffusion Models
In the field of image generation, Diffusion Models have emerged as a strong alternative to GANs. These models work by gradually transforming random noise into a coherent image, step by step, through a simulated diffusion process.
OpenAI’s DALL·E and Stability AI’s Stable Diffusion have demonstrated how diffusion models can generate high-quality images from text descriptions.
Practical Applications of Generative AI
Generative AI has been applied across many fields, each showing the transformative potential of this technology:
Content Creation
Generative AI assists artists, designers, and writers in producing new works in various artistic styles. Similarly, AI can support musicians and composers. Platforms like OpenAI’s MuseNet and Jukedeck have shown that AI can compose original music in multiple genres.
Healthcare and Drug Development
Generative AI models have shown great promise in drug development and molecular design. By creating new chemical compounds or optimizing protein structures, Generative AI helps speed up the drug discovery process.
Generative models can predict how molecules interact within the body, simulate biological interactions, and even create new biomaterials. Companies like Insilico Medicine and Atomwise are using AI to advance drug discovery.
Synthetic Data Generation
Generative AI is also being used to create synthetic data for training other machine learning models, especially in situations where real data is scarce or privacy concerns exist.
For instance, GANs have been employed to generate synthetic medical X-ray images, enabling the training of diagnostic models without violating patient privacy. Generative AI is also useful for autonomous vehicles, where simulations can be created to train self-driving cars under various conditions.
Gaming and Virtual Reality
In the gaming and virtual reality (VR) industries, Generative AI is being leveraged to create immersive, dynamic environments, characters, and scenarios. AI-driven procedural content generation (PCG) can be used to design virtually limitless game worlds, enhancing player experience and interaction. This technology also allows for the automatic creation of personalized gameplay experiences based on user behavior.

Marketing and Advertising
Generative AI has significant applications in marketing and advertising. It can be used to generate personalized content, including advertisements, email campaigns, and social media posts, tailored to individual preferences. By analyzing customer data and behavior, Generative AI can create optimized content that resonates with target audiences and improves engagement. Furthermore, AI-generated graphics and videos can save time and resources for marketers, enabling them to scale their campaigns effectively.
Education
Generative AI has transformative potential in education by helping create personalized learning experiences for students. AI can generate customized lesson plans, quizzes, and learning materials based on individual student progress and needs. Additionally, AI-powered tutoring systems can provide real-time feedback, helping students improve their understanding of various subjects.
Art and Creative Industries
Generative AI has made a remarkable impact on the art world, allowing artists to explore new creative possibilities. AI tools can generate paintings, music, sculptures, and other forms of art based on specific styles or themes. Artists can use these tools as collaborators to push the boundaries of traditional creativity and experiment with new forms of expression.
The Future of Generative AI: Challenges and Opportunities
While the potential of Generative AI is vast, there are several challenges and ethical considerations that need to be addressed:
- Data Privacy and Security: Since Generative AI often relies on vast datasets, including personal data, ensuring privacy and data security is critical. Models must be designed to avoid misuse of sensitive information.
- Bias and Fairness: Like other AI models, Generative AI can inherit biases from the data it’s trained on. Ensuring that Generative AI systems are fair and free from harmful biases is essential, especially when used in applications like hiring, healthcare, and law enforcement.
- Intellectual Property: The question of who owns the content generated by AI remains a significant legal challenge. As AI systems become more capable of producing creative work, determining intellectual property rights for AI-generated content will require new legal frameworks.
- Human-AI Collaboration: Rather than replacing human creativity, Generative AI has the potential to augment it. The future of this technology lies in enhancing human capabilities and fostering collaboration between AI and humans to create more innovative and impactful results.
Generative AI is rapidly evolving and revolutionizing industries with its ability to create novel content that mimics human creativity. As the technology continues to advance, its applications will expand across more domains, offering exciting opportunities for innovation and transformation. By understanding its potential and challenges, businesses and individuals can better prepare for the future of AI.
>>> READ MORE: 2025 technology trends: The explosive development of AI Agents