AI Agents are artificial intelligence systems that can interact with the environment and make decisions to achieve goals in the real world without any human guidance or intervention. This technology are shaping technology trends, with notable milestones such as the Google I/O 2023 event launching Astra or the emergence of GPT-4o.
Large corporations are pouring billions of dollars into AI Agents to take the lead in AI Era. In this article, FPT.AI will clarify how AI Agents are helping businesses improve processes, enhance customer experience and optimize operations.
What are AI Agents (Intelligent Agents)?
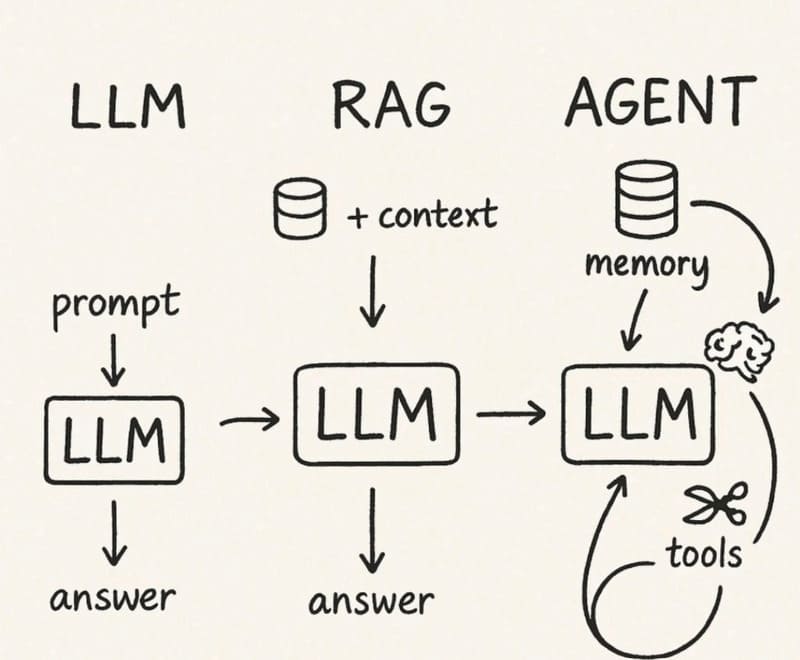
AI Agents are artificial intelligence systems that can interact with the environment and make decisions in the real world without any human guidance or intervention.
AI Agents can gather information from their surroundings, design their own workflows, use available tools, coordinate between different systems, and even work with other Agents to achieve goals without requiring user supervision or continuous new instructions.
With the development of Generative AI, Natural language processing, Foundation Models, and Large Language Models (LLMs), AI Agents can now simultaneously process multiple types of multimodal information such as text, voice, video, audio, and code. Advanced agent AI can learn and update their behavior over time, continuously experimenting with new solutions to problems until achieving optimal results. Notably, they can detect their own errors and find ways to correct them as they progress.
AI Agents can exist in the physical world (robots, autonomous drones, or self-driving cars) or operate within computers and software to complete digital tasks. The aspects, components, and interfaces of each agent AI can vary depending on its specific purpose. Encouragingly, even people without deep technical backgrounds can now build and use AI Agents through user-friendly platforms.

>>> READ NOW: What is Generative AI? Trends in Applying GenAI from 2024 to 2027
What are the key features of an AI Agent platform?
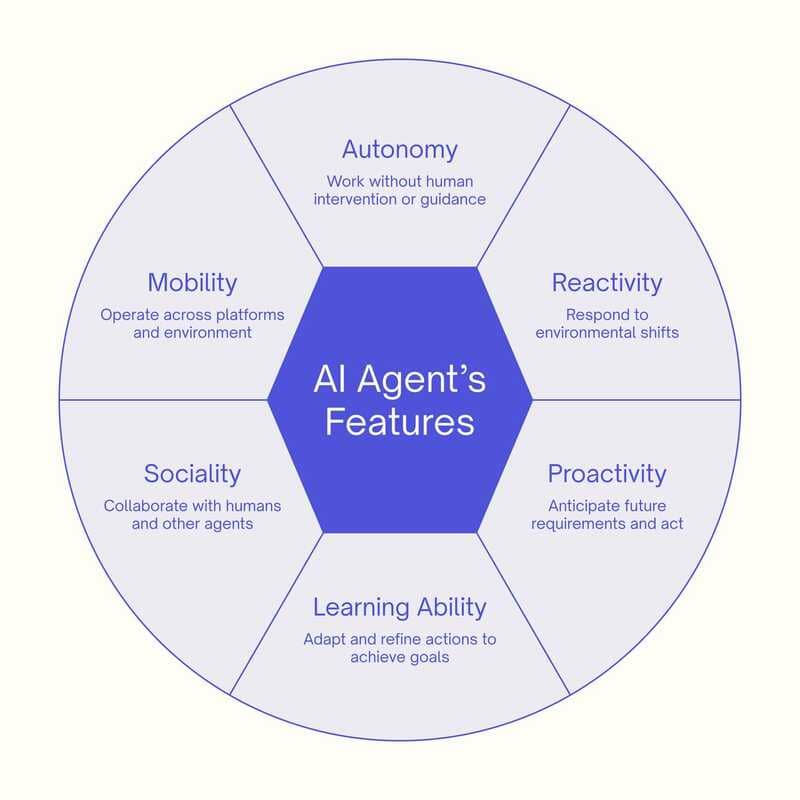
Key features of an AI Agent platform include:
- Autonomy: AI Agents can operate independently, make decisions, and take actions without continuous human supervision. For example, self-driving cars can adjust speed, change lanes, stop, or adjust routes based on real-time sensor data about road conditions and obstacles, without driver intervention.
- Reasoning Ability: AI agents use logic and analyze available information to draw conclusions and solve problems. They can identify patterns in data, evaluate evidence, and make decisions based on the current context, similar to human thinking processes.
- Continuous Learning: AI Agents continuously improve their performance over time by learning from data and adapting to changes in the environment. For instance, customer support chatbots can analyze millions of conversations to gain deeper understanding of common issues and improve the quality of proposed solutions.
- Environmental Observation: AI agents continuously collect and process information from their surroundings through techniques like computer vision, natural language processing, and sensor data analysis. This ability helps them understand the current context and make appropriate decisions.
- Action Capability: AI agents can perform specific actions to achieve goals. These actions can be physical (like a robot moving objects) or digital (like sending emails, updating data, or triggering automated processes).
- Strategic Planning: AI agents can develop detailed plans to achieve goals, including identifying necessary steps, evaluating alternatives, and selecting optimal solutions. This ability requires predicting future outcomes and considering potential obstacles.
- Proactivity and Reactivity: AI agents proactively anticipate and prepare for future changes. For example, Nest Thermostat learns the homeowner’s heating habits and proactively adjusts temperature before the user returns home, while quickly responding to unusual temperature fluctuations.
- Collaboration Ability: AI agents can work effectively with humans and other agents to achieve common goals. This collaboration requires clear communication, coordinated actions, and understanding the roles and objectives of other participants in the system.
- Self-Improvement: Advanced AI agents can self-evaluate and improve their operational performance. They analyze the results of previous actions, adjust strategies based on feedback, and continuously enhance their capabilities through machine learning techniques and optimization.
>>> READ NOW: 2 Ways to Classify Artificial Intelligence and 7 Common Types of AI
Differences between Agentic AI Chatbots and AI Chatbots
Below is a comparison table highlighting the distinctions between Agentic AI chatbots and AI Chatbots:
| Criteria | Agentic AI Chatbots | Traditional AI Chatbots |
| Autonomy | Operate independently, perform complex tasks without continuous intervention | Require continuous guidance from users, only respond when prompted |
| Memory | Maintain long-term memory between sessions, remember user interactions and preferences | Limited or no memory storage capability, each session typically starts from scratch |
| Tool Integration | Use function calls to connect with APIs, databases, and external applications | Operate in closed environments with no ability to access external tools or data sources |
| Task Processing | Break down complex tasks into subtasks, execute them sequentially to achieve goals | Only process simple, individual requests without ability to decompose complex problems |
| Knowledge Sources | Combine existing knowledge with new information from external sources (RAG) | Rely solely on pre-trained data, unable to update with new information |
| Learning Capability | Continuously learn from interactions, improving accuracy and relevance over time | Do not learn or improve from user interactions, responses always follow fixed patterns |
| Operation Mode | Can perform multiple processing rounds for a single request, creating multi-step workflows | Operate on a single-turn basis (receive-process-respond), without multi-step capabilities |
| Planning Ability | Strategically plan and self-adjust when encountering new information or obstacles | No long-term planning capability or strategy adjustment |
| Personalization | Provide personalized experiences based on user history, preferences, and context | Deliver generalized responses, identical for all users |
| Response Process | Analyze intent, access relevant information, create plan, execute actions, and evaluate results | Recognize patterns, search for appropriate responses in existing database, reply |
| Error Handling | Recognize errors, self-correct, and find alternative solutions when problems arise | Often fail to recognize errors or lack ability to recover when encountering off-script situations |
| User Interaction | Proactively ask clarifying questions, suggest options, and track progress | Passive, only directly respond to what users explicitly ask |
| Workflow | Use threads to store all information, connect with tools, execute function calls when needed | Simple processing according to predefined scripts, no workflow extension capability |
| Practical Applications | Complex customer support, data analysis, process automation, personal assistance | Primarily for FAQs, basic customer support, simple conversations |
| Intent Detection | Accurately identify users’ underlying intents, even when not explicitly stated | Only react to specific keywords or patterns, often missing true intentions |
| System Integration | Easily integrate with multiple systems and applications through APIs | Limited integration capabilities, often requiring custom solutions |
| Development Requirements | Can be developed on no-code platforms, without requiring in-depth programming knowledge | Typically require programming knowledge to build and maintain |
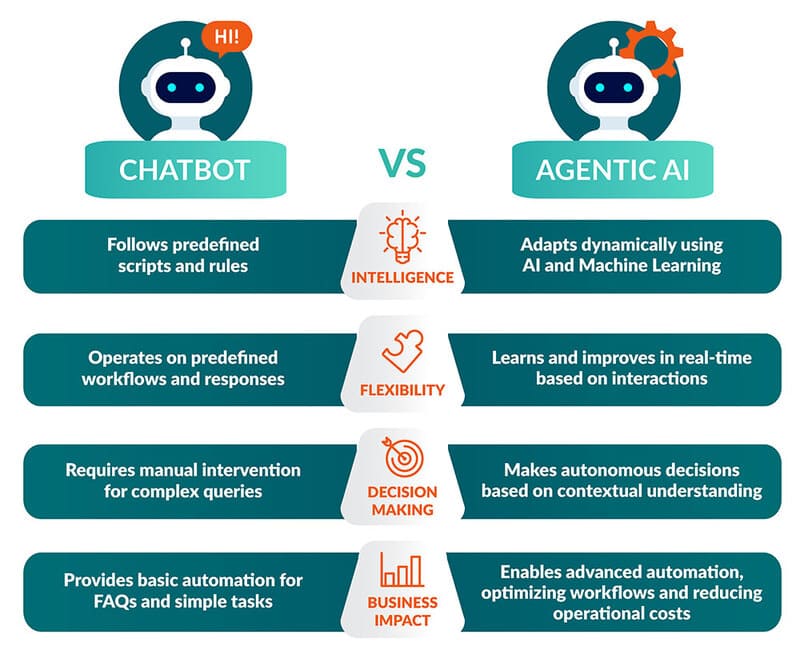
Agentic AI chatbots mark a significant evolution in conversational AI, powered by LLMs but extending well beyond them. Operating on thread-based architecture, they store complete conversation histories, files, and function call results. These advanced chatbots activate via various triggers (scheduled events, database changes, or manual inputs) to analyze requests, interpret intentions, and execute actions autonomously.
Five key innovations drive this technology:
- RAG integration for context-aware responses with higher accuracy
- Function calling to interact with external systems
- Advanced memory systems for continuous learning and adaptation
- Tool evaluation to assess resources and fill information gaps
- Subtask generation to break down complex goals independently
Unlike traditional chatbots’ single-turn model (receive-process-respond), agentic chatbots process multiple turns per prompt, queue actions strategically, and dynamically select appropriate tools based on user intent. They can search connected knowledge bases, call external APIs, or generate responses from core training when external tools aren’t needed. Critically, no-code platforms have democratized their development, accelerating adoption across industries by enabling businesses of all sizes to implement sophisticated AI without significant technical investment.
>>> READ MORE: What is Agentic RAG? Difference between Agentic RAG and RAG
Key Components of AI Agents
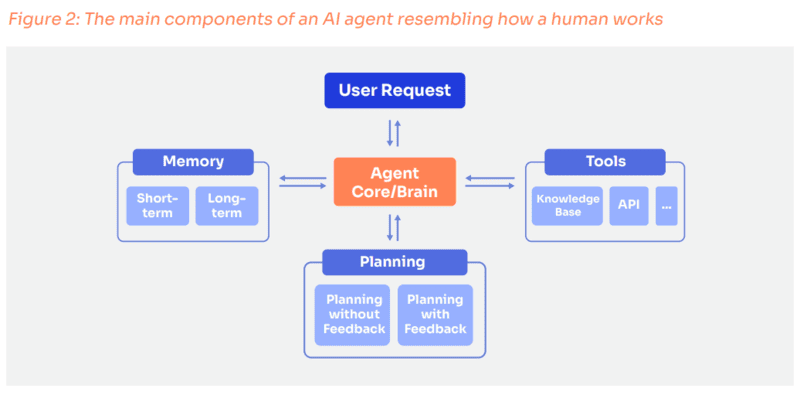
AI Agents are composed of multiple components working together as a unified system, similar to how the human body functions with senses, muscles, and brain. Each component in AI Agent Architecture plays a specific role in helping the agent sense, think, and interact with the surrounding world.
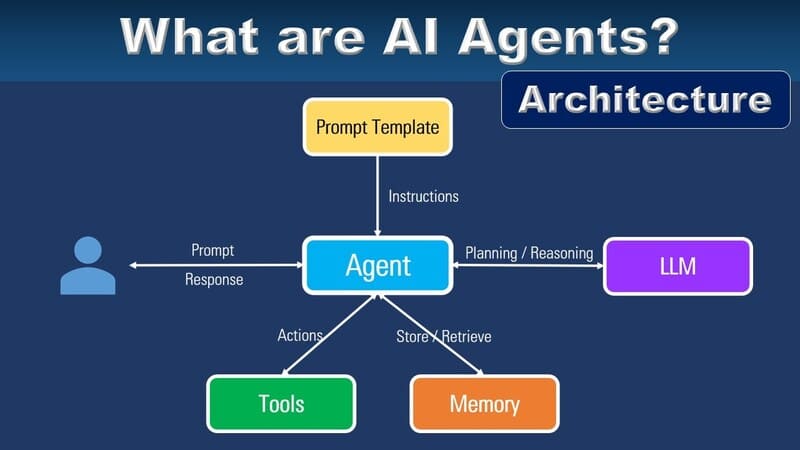
Sensors
Sensors help AI Agents collect information (percepts) from the surrounding environment to understand the context and current situation. In physical robots, sensors might be cameras for “seeing,” microphones for “hearing,” or thermal sensors for “feeling” temperature. For software agents running on computers, sensors might be web search functions to gather online information, or file reading tools to process data from PDF documents, CSV files, or other formats.
>>> EXPLORE MORE: How to build an AI Agent and train it successfully?
Actuators
If sensors are how agents receive information, actuators are how they affect the world. Actuators are components that allow agents to perform specific actions after making decisions. In physical robots, actuators might be wheels for movement, mechanical arms for lifting objects, or speakers for producing sound. For software agents, actuators might be the ability to create new files, send emails, control other applications, or modify data in systems.
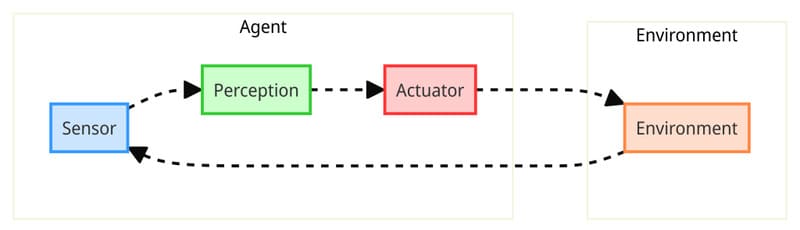
Brain
Processors, Control Systems, and Decision-Making Mechanisms form the “brain” of the AI Agents, where information is processed and decisions are made. Processors analyze raw data from sensors and convert it into meaningful information. Control systems coordinate the agent’s activities, ensuring all parts work harmoniously. Decision-making mechanisms are the most important part, where the agent “thinks” about processed information, evaluates different action options, and selects the most optimal action based on goals and existing knowledge.
>>> EXPLORE: Applications of AI Agents in Personalized Marketing
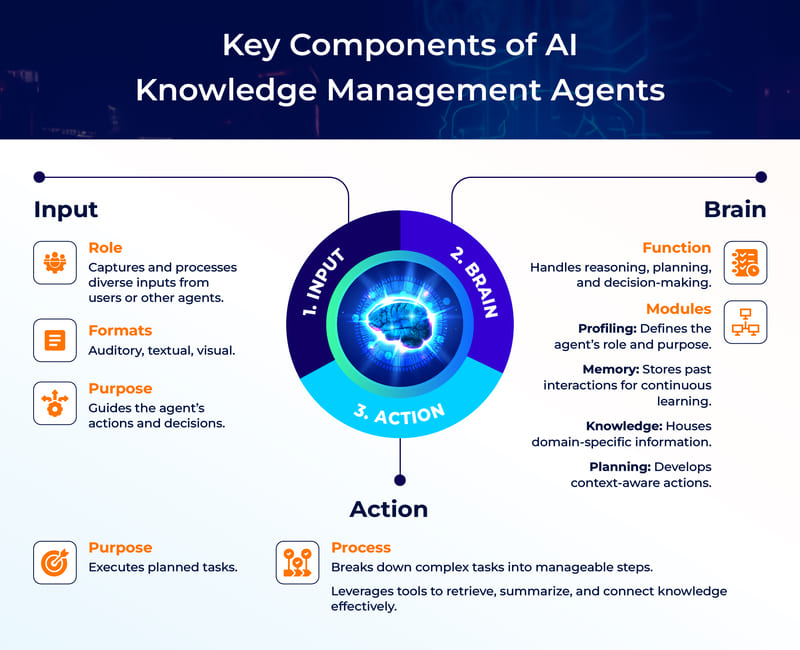
Learning and Knowledge Base Systems
These are the memory and learning capabilities of AI Agents, allowing them to improve performance over time. Knowledge base systems store information the agent already knows: data about the world, rules of action, and experiences from previous interactions. This might be a database of locations, events, or problems the agent has encountered along with corresponding solutions.
Learning systems allow the agent to learn from experience, recognize patterns, and improve decision-making abilities. An agent with learning capabilities will continuously update its knowledge base, helping it better cope with new situations or changes in the environment.
The complexity level of these components depends on the tasks the AI Agent performs. A smart thermostat might only need simple temperature sensors, a basic control system, and actuators to turn heating systems on/off. In contrast, a self-driving car needs to be equipped with all components at high complexity levels: diverse sensors to observe roads and other vehicles, powerful processors to handle large amounts of real-time data, sophisticated decision-making systems for safe navigation, precise actuators to control the vehicle, and continuous learning systems to improve driving capabilities through each experience.
>>> EXPLORE: What Are Intelligent Agents? The Difference Between AI Agents and Intelligent Agents
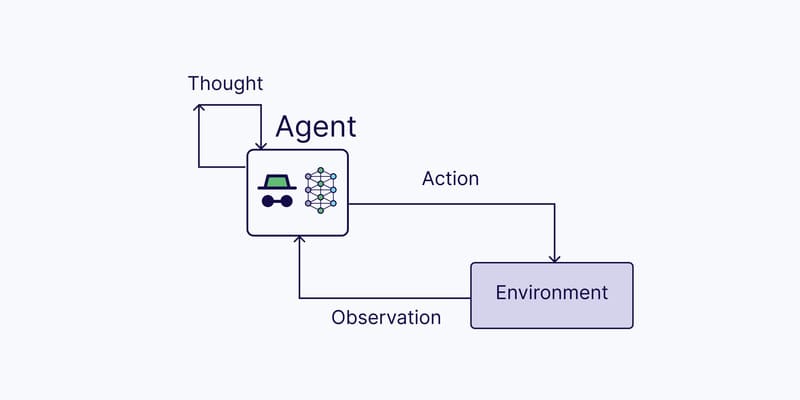
How do AI Agents Work?
When receiving a command (goal) from a user (Prompt), AI Agents immediately initiate the goal analysis process, transferring the prompt to the core AI model (typically a Large Language Model) and beginning to plan actions. The Agent will break down complex goals into specific tasks and subtasks, with clear priorities and dependencies. For simple tasks, the Agent may skip the planning stage and directly improve responses through an iterative process.
During implementation, thanks to Sensors, AI agents collect information (transaction data, customer interaction history) from various sources (including external datasets, web searches, APIs, and even other agents). During this collection process, the AI Agent continuously updates its knowledge base, self-adjusts, and corrects errors if necessary.
The Processors of AI Agents use algorithms, Deep Neural Networks, machine learning models, and artificial intelligence to analyze information and calculate necessary actions.
Throughout this process, the agent’s Memory continuously stores information (such as history of decisions made or rules learned). Additionally, AI Agents also use feedback from users, feedback from other Agents, and Human-in-the-loop (HITL) to self-compare, adjust, and improve performance over time, avoiding repetition of the same errors.
Finally, through Actuators, AI Agents perform actions based on their decisions. For robots, actuators might be parts that help them move or manipulate objects. For software agents, this might be sending information or executing commands on systems.
To illustrate this process, imagine a user planning their vacation. They ask an AI Agent to predict which week of the coming year will have the best weather for surfing in Greece. Since the large language model that underpins the agent is not specialized in weather forecasting, the agent must access an external database that contains daily weather reports in Greece over the past several years.
Even with historical data, the agent cannot yet determine the optimal weather conditions for surfing. Therefore, it must communicate with a surf agent to learn that ideal surfing conditions include high tides, sunny weather, and low or no rainfall.
With the newly gathered information, the agent combines and analyzes the data to identify relevant weather patterns. Based on this, it predicts which week of the coming year in Greece is most likely to have high tides, sunny weather, and low rainfall. The final result is then presented to the user.
>>> READ NOW: RPA vs AI Agents: Is RPA Still Relevant in the Age of AI?
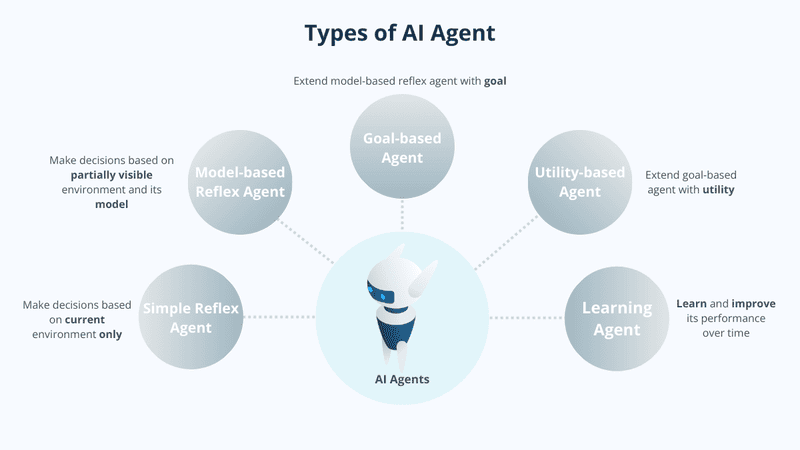
Common Types of AI Agents
There are 5 primary types of AI Agents: Simple Reflex Agents, Goal-Based AI Agents, Model-Based Reflex Agents, Utility-Based Agents, Learning Agents. Each suited to specific tasks and applications:
- Simple Reflex Agents: Simple Reflex Agents operate on the “condition-action” principle and respond to their environment based on simple pre-programmed rules, such as a thermostat that turns on the heating system at exactly 8pm every night. The agent does not retain any memory, does not interact with other agents without information, and cannot react appropriately if faced with unexpected situations.
- Model-Based Reflex Agents: Model-Based Reflex Agents use their cognitive abilities and memory to create an internal model of the world around them. By storing information in memory, these agents can operate effectively in changing environments but are still constrained by pre-programmed rules. For example, a robot vacuum cleaner can sense obstacles when cleaning a room and adjust its path to avoid collisions. It also remembers areas it has cleaned to avoid unnecessary repetition.
- Goal-Based AI Agents: Goal-Based Agents are driven by one or more specific goals. They look for appropriate courses of action to achieve the goal and plan ahead before executing them. For example, when a navigation system suggests the fastest route to your destination, it analyzes different paths to find the most optimal one. If the system detects a faster route, it updates and suggests an alternative route.
- Utility-Based Agents: Utility-Based Agents evaluate the outcomes of decisions in situations with multiple viable paths. They employ utility functions to measure the usefulness that each action might bring. Evaluation criteria typically include progress toward goals, time requirements, or implementation complexity. This evaluation system helps identify the ideal choice: Is the best option the cheapest? The fastest? The most efficient? For example, a navigation system considers factors such as fuel economy, reduced travel time, and toll costs to select and recommend the most favorable route for the user.
- Learning Agents: Learning Agents learn through concepts and sensors, while utilizing feedback from the environment or users to improve performance over time. New experiences are automatically added to the Learning Agent’s initial knowledge base, helping the agent operate effectively in unfamiliar environments. For example, e-commerce websites use Learning Agents to track user activity and preferences, then recommend suitable products and services. The learning cycle repeats each time new recommendations are made, and user activities are continuously stored for learning purposes, helping Agents improve the accuracy of their suggestions over time.
>>> EXPLORE: What is an LLM Agent? How it works, advantages, and disadvantages
What are the outstanding benefits of using AI Agents?
AI Agents for businesses deliver a consistent experience to customers across multiple channels, with the following 4 outstanding benefits:
- Improve productivity: AI Agents help automate repetitive and time-intensive tasks, freeing up human resources from manual work so that businesses can focus on more strategic, creative and high-value initiatives, fostering innovation. For more complex issues, AI Agents can intelligently escalate cases to human agents. This seamless collaboration ensures smooth operations, even during periods of high demand.
- Reduce costs: By optimizing processes and minimizing human errors, AI personnel help businesses cut operating costs. Complex tasks are handled efficiently by AI Agents without the need for constant human intervention.
- Make informed decisions: AI Agents use machine learning (ML) technologies to help managers collect and analyze data (product demand or market trends) in real time, making faster and more accurate decisions.
- Improve customer experience: AI agents significantly enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty by offering round-the-clock support and personalized interactions. Their prompt and precise responses effectively address customer needs, ensuring a smooth and engaging service experience. Lenovo leveraged AI agents to streamline product configuration and customer service, integrating them into key systems like inventory tracking. By building a knowledge database from purchase data, product details, and customer profiles, AI agents help Lenovo cut setup time from 12 minutes to 2 minutes, boosting sales productivity and customer experience. This led to a 12% improvement in order delivery KPIs (within 17 days) and generated $5.88 million in one year, according to Gartner.
>>> Read more about: AI Agents at Work – Foundation for Productivity Breakthrough
Is ChatGPT an AI Agent?
ChatGPT is not an AI Agent. It is a large language model (LLM) designed to generate human-like responses based on received input, with some components similar to AI Agents:
- Simple sensors that receive text input
- Actuators that generate text, images, or audio
- Control system based on transformer architecture
- Knowledge base system from pre-training data and fine-tuning.
However, these elements are not sufficient to make ChatGPT a genuine Agent. The most important difference between AI Agents and ChatGPT is autonomy. ChatGPT cannot set its own goals, make plans, or take independent actions. When you ask ChatGPT to write an email, it can create content but cannot send the email itself or evaluate whether sending an email is the best action in a specific situation.
Additionally, ChatGPT cannot directly interact with external systems or adjust its behavior based on real-time feedback. Updates like plugins, extended frameworks, APIs, and prompt engineering can improve ChatGPT’s functionality, but still don’t create a complete Agent. ChatGPT also lacks the ability to maintain long-term memory between sessions. It doesn’t “remember” you or previous conversations unless specifically programmed to do so in certain applications.
>>> READ NOW: What is a Multi Agent System (MAS)?
Practical Applications of AI Agents
Imagine a future workplace where every employee, manager, and leader not only works together, but is also equipped with a team of AI teammates to support them in every task and at every moment of the workday. With these AI teammates, we will become 10x more productive, achieve better results, create higher quality products, and of course, become 10x more creative.
You may be wondering, “When will this future come?” The answer from FPT is: The future is now. Here are four stories that demonstrate how AI is already impacting businesses.
Revolutionizing Insurance Claims Processing
Imagine you go to the hospital for a health check-up, buy medicine, and file an insurance claim. Typically, the insurance company’s document processing will take at least 20 minutes. With integrated AI Agents, insurers can process all documents through rapid assessment tools, risk assessment tools, and fraud detection tools, returning results in just 2 minutes.
This represents an incredible leap in productivity, improving the customer experience and creating new competitive value for the business.
>>> READ NOW: Blockchain, Deepseek & AI Agents Reshape the AI Race
Transforming the Customer Contact Center
The second story focuses on customer service. Several FPT.AI customers have deployed AI systems for inbound and outbound communications. These systems provide human-like customer support, handling requests, resolving issues, and providing excellent service.
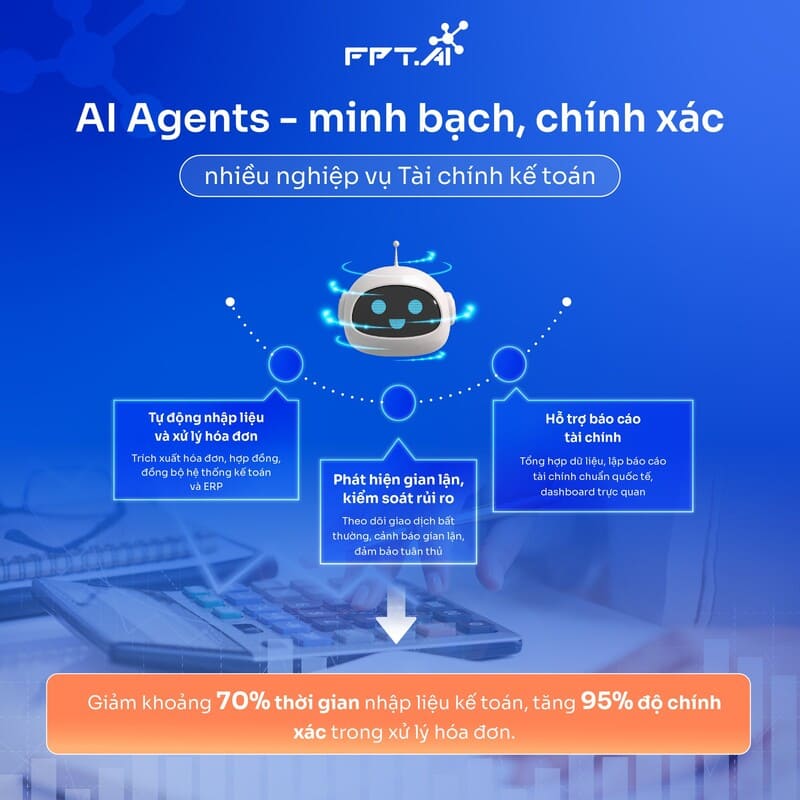
For some customers, AI Agents are now handling 70% of customer requests, completing 95% of received tasks, and achieving a customer satisfaction rating of 4.5/5. Currently, FPT’s customer service AI Agents manage 200 million user interactions per month.


Empowering pharmacists with AI Mentor
At Long Chau, the largest pharmacy chain in Vietnam, more than 14,000 pharmacists work every day to advise customers. To ensure they stay updated with knowledge and work effectively, FPT.AI has developed an AI Mentor that interacts with more than 16,000 pharmacists across 2,000 pharmacies every day.
This AI Mentor identifies strengths and weaknesses, provides insights, and personalizes conversations to help them improve. The results are:
- Pharmacists’ competencies improved by 15%.
- Productivity increased by 30%.
Within the first nine months of the year, the pharmacy chain recorded a revenue growth of 62%, reaching VND 18.006 trillion, accounting for 62% of FRT’s total revenue and completing 85% of its 2024 plan. More importantly, we pride ourselves on helping pharmacists become the best versions of themselves while continuously improving.
>>> READ NOW: Understanding AI Agents in KYC
From a cost center to a profit center
FPT.AI’s AI Innovation Lab works with customers to identify opportunities, deploy pilots, and scale solutions. For example, one of our clients transformed their customer service center from a cost center to a profit center.
Using AI, they detected when customers were happy and immediately suggested appropriate products or services to upsell credit cards, cross-sell overdrafts, activate new customers to sign up, and reactivate existing customers. This approach helped the customer service center contribute about 6% of total revenue.
The four stories above are just a small part of the countless ways AI can transform businesses. AI, as a new competitive factor, is opening up a blue ocean of innovation. Every company and organization will need to reinvent their operations and build a strong foundation to compete in the future, leveraging the advances of AI.

>>> EXPLORE: What is Agentic AI? The differences between Generative AI and Agentic AI
Challenges in Deploying AI Agents
AI Agents are still in their early stages of development and face many major challenges. According to Kanjun Qiu, CEO and founder of AI research startup Imbue, the development of AI Agents today can be compared to the race to develop self-driving cars 10 years ago. Although AI Agents can perform many tasks, they are still not reliable enough and cannot operate completely autonomously.
One of the biggest problems that AI Agents face is the limitation of logical thinking. According to Qiu, although AI programming tools can generate code, they often write wrong or cannot test their own code. This requires constant human intervention to perfect the process.
Dr. Fan also commented that at present, we have not achieved an AI Agent that can fully automate daily repetitive tasks. The system still has the ability to “go crazy” and not always follow the exact user request.

Another major limitation is the context window – the ability of AI models to read, understand, and process large amounts of data. Dr. Fan explains that models like ChatGPT can be programmed, but have difficulty processing long and complex code, while humans can easily follow hundreds of lines of code without difficulty.
Companies like Google have had to improve the ability to handle context in their AI models, such as with the Gemini model, to improve performance and accuracy.
For “physical” AI Agents such as robots or virtual characters in games, training them to perform human-like tasks is also a challenge. Currently, training data for these systems is very limited and research is just beginning to explore how to apply generative AI to automation.
>>>> EXPLORE: What is Data Leakage? How to Prevent Data Leakage when implementing Generative AI?
Continue writing the future with AI Agents with FPT.AI
In the digital economy, competition between companies and countries is no longer based solely on core resources, technology and expertise. Organizations, from now on, will need to compete with a new important factor: AI Companions or AI Agents.
It is expected that by the end of 2025, there will be about 100,000 AI Agents accompanying businesses in customer care, operations and production. Each AI Agent will undertake a number of tasks such as programming, training, customer care… Thanks to that, employees are more empowered, businesses increase operational productivity, improve customer experience, and make more accurate decisions based on data analysis.

FPT AI Agents – a platform that allows businesses to develop, build and operate AI Agents in the simplest, most convenient and fastest way. The main advantages of FPT AI Agents include:
- Easy to operate and use natural language.
- Flexible integration with enterprise knowledge sources.
- AI models are optimized for each task and language.
Currently, FPT AI Agents supports 4 languages: English, Vietnamese, Japanese and Indonesian. In particular, AI Agents have the ability to self-learn and improve over time.

AI Agents are all operated on FPT AI Factory – an ecosystem established with the mission of empowering every organization and individual to build their own AI solutions, using their data, supplementing their knowledge and adapting to their culture. This differentiation fosters a completely new competitive edge among enterprises and extends to building AI sovereignty among nations.
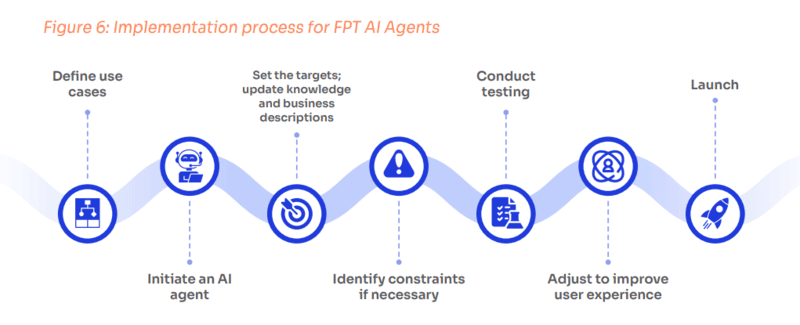
With more than 80 cloud services and 20 AI products, FPT AI Factory helps accelerate AI applications by 9 times thanks to the use of the latest generation GPUs, such as H100 and H200, while saving up to 45% in costs. These factories are fully compatible with the NVIDIA AI Enterprise platform and architectural blueprints, ensuring seamless integration and operation.
>>> READ NOW: Why Gen AI Agents are the future prospect of Generative AI?